The Silent Recyclers: Unveiling the Enigmatic Realm of Fungi and Lichens
Beyond Photosynthesis: How Fungi and Their Symbiotic Partners Engineering the Earth’s Nutrient Cycle.

🧬 Introduction: The Non-Photosynthetic Rebellions
Up until now, our journey through botany has focused on “green” life. But in Episode 6, we encounter a massive group that breaks the rules: The Fungi . These are eukaryotic organisms with cell walls, but they lack the one thing that defines a plant—Chlorophyll.
Because they cannot produce their own food, fungi have mastered the art of being heterotrophs. They live as saprophytes (decomposing dead matter), parasites (living off others), or as ingenious mutualists. From the microscopic yeast to the sprawling networks of forest mushrooms, fungi are the essential “cleanup crew” of our planet.
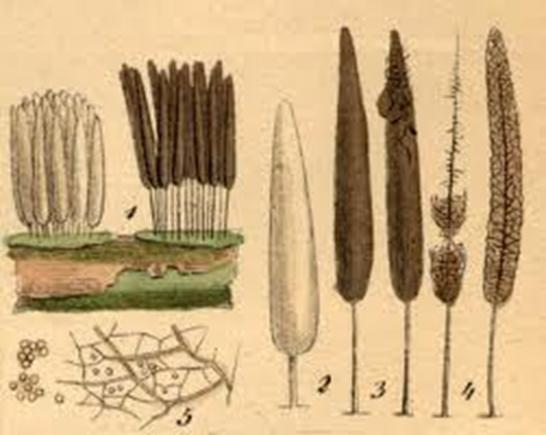
I. Myxomycota: The Shape-Shifters (The Slime Molds)
Before we get to “true” fungi, we must look at the Myxomycota. These strange organisms exist on the border between the animal and fungal kingdoms.
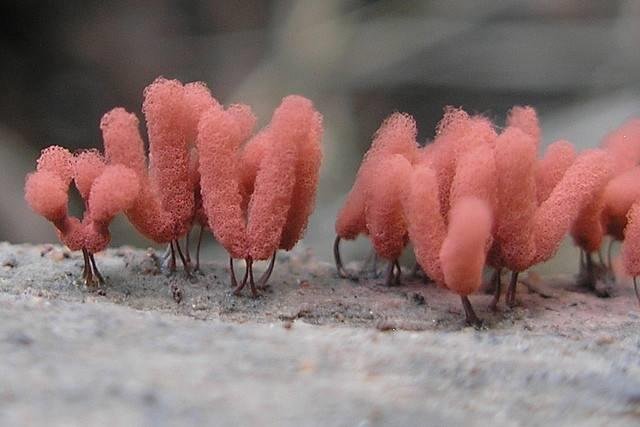

- Animal-like: Their vegetative body is a naked mass of protoplasm called a plasmodium, which can move and “eat” bacteria and organic bits.
- Plant-like: When it’s time to reproduce, they stop moving and grow fixed structures that produce spores with rigid cell walls.
- Representative: Stemonitis , often found as dark, hair-like clusters on rotting wood.
II. Eumycota: The True Fungi and Their Structural Logic
The Eumycota is the heart of mycology. Their “body” is not made of tissues like plants, but of a network of filaments called Hyphae. A mass of these hyphae is known as a Mycelium .
1. Advanced Architecture:
- Septate vs. Coenocytic: Some fungi have walls (septa) between their cells, while others are essentially one long, multi-nucleated tube.
- Cell Wall: Unlike plants (cellulose), most fungal cell walls are made of Chitin—the same tough material found in shrimp shells!
2. Triple-Threat Reproduction:
Fungi are reproduction experts, using Vegetative (fragmentation), Asexual (producing various spores like zoospores or conidia), and Sexual methods. The sexual cycle involves the fusion of nuclei to form specialized structures like Zygospores, Ascospores, or Basidiospores.
III. The Major Fungal “Clubs”
The PDF outlines four key groups within the Eumycota:
- Chytridiomycota : The most primitive, retaining flagellated swimming spores—a link to their aquatic ancestors.
- Zygomycota : Fast growers like Rhizopus (Black Bread Mold. They are famous for their tough, thick-walled Zygospores.
- Ascomycota : A massive group including Yeasts (Saccharomyces), Penicillium (source of life-saving antibiotics), and delicious morels. They produce spores inside a sac-like structure called an Ascus .
- Basidiomycota : The “poster children” of fungi. This includes all mushrooms, toadstools, and puffballs. They produce spores on a club-shaped structure called a Basidium .
IV. Lichens: The Ultimate Biological Marriage
Perhaps the most fascinating part of the material is the Lichen . A lichen is not a single organism, but a symbiotic partnership.
- The Alga (Photobiont): Usually a Green Alga or Cyanobacteria. It provides the “food” through photosynthesis.
- The Fungus (Mycobiont): Usually an Ascomycete. It provides the “house,” protection, and absorbs minerals and water.
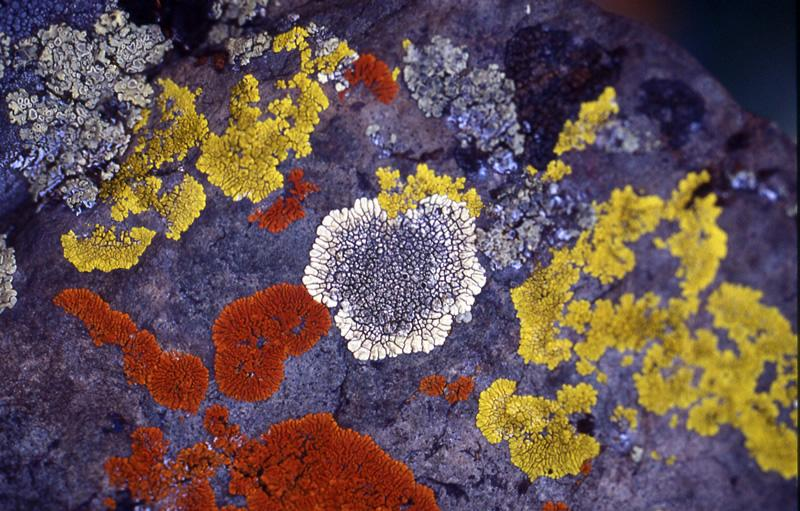
Forms of Lichens:
- Crustose : Flat and tightly attached to rocks (e.g., Graphis).
- Foliose : Leaf-like and somewhat loose (e.g., Parmelia).
- Fruticose : Hair-like or shrubby, either upright or hanging (e.g., Usnea).
V. Fungi in the Human World: Good, Bad, and Beautiful
Fungi are dual-edged swords. On one hand, they are essential for Food Production (bread, beer, edible mushrooms) and Medicine (Antibiotics). On the other, they are responsible for Plant Diseases (like rusts and smuts) and can destroy crops. However, without their role in the global carbon cycle as decomposers, life on Earth would quickly stall.